Measuring our body temperature is not new to us, but have you wondered how we check the temperature of other objects? Our household thermometer won’t be enough to measure this, therefore we must use a temperature sensor.
What is a temperature sensor?
A temperature sensor is a device used to measure the temperature of the air, liquid or solid matter. There are different kinds of temperature sensors available, and each type operates on a different working principle. The primary use of a temperature sensor, in conjunction with a controller, is to help maintain a system’s temperature between a set range. Based on its working principle, the output signal of a temperature sensor plays a vital role in maintaining a specific temperature within any equipment or process. When the temperature sensor reads a temperature that drifts away from the set range on the controller, the controller sends the signal to heat or cool depending on the reading. One may find them present in our everyday life as well as in industrial processes.
Types of Temperature Sensors
There are many types of temperature sensors that use different technologies and principles to measure temperature. There are two broad categories of temperature sensors – contact and non-contact type.
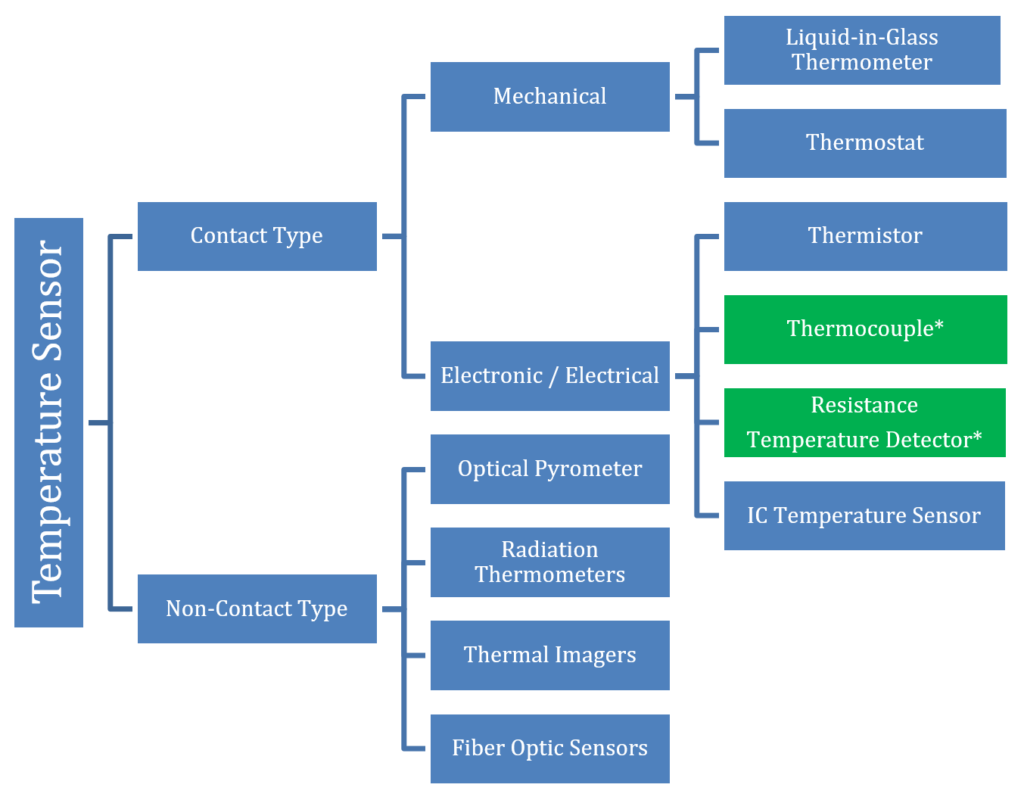
Contact Temperature Sensors
When a temperature sensor comes in physical contact with an object, the temperature conducts and gives out a signal to control the targeted temperature of a process. There are two major categories of contact-type temperature sensors: Mechanical Sensors & Electronic / Electrical Sensors.
- Mechanical type: When a change in temperature causes mechanical motion and produces signal through a visible scale or through connecting or disconnecting a circuit loop, it is called a mechanical-type temperature sensor. Liquid-in-glass thermometers and Thermostats comprise a large percentage of this category.
- Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers:
- It is the most well-known temperature sensor that we use in our daily life as its most common application is to measure body temperature in the medical field. The working principle is the expansion of the liquid inside a glass tube due to the rise in temperature. The temperature scale is calibrated based on the rate of thermal expansion of the liquid material and the diameter of the tube used. Mercury and alcohol are more commonly used as the liquid material in this sensor. Another common use for this type of temperature sensor is to check the temperature of a liquid such as food or water.
- Thermostat:
- A thermostat is a switch that is generally made up of two different metals, such as brass-iron or other engineered alloys, that are bonded together to form a bi-metallic strip. The different metals in the bi-metallic strip have different thermal expansion coefficients thus causing the strip to curl in the same direction when the temperature rises and in the opposite direction when the temperature drops. The thermostat disconnects the circuit when it reaches a set temperature and reconnects again when the temperature deviates away from the set threshold. There are a wide variety of use-cases for a thermostat; these are commonly seen in refrigerators and air conditioning units.
- Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers:
- Electronic / Electrical Type: Thermistors, Thermocouples, RTDs (Resistance Temperature Detector), and IC temperature sensor are examples of electronic / electrical type temperature sensors.
- Thermistor:
- Thermistors consist of a sensing element that can be either glass or epoxy coated. They have 2 wires which can be connected to an electric circuit. They measure temperature by measuring the change in resistance of electric current and display precise, predictable, and large changes in the alteration of various temperatures. We can find thermistors in our everyday appliances such as fire alarms, refrigerators, ovens, etc. Thermistors are usually not too expensive. There are two types of thermistors available in the market: NTC (Negative Temperature Co-efficient) type and PTC (Positive Temperature Co-efficient) type.
- Thermocouple:
- A thermocouple sensor consists of two different metals joined together at one end to form a junction. When this junction of the two dissimilar metals is heated or cooled, a voltage is being developed that is directly proportional to the temperature difference. This thermoelectric effect is known as the Seebeck effect. Thermocouples can operate in the most extensive temperature range from -200 to 1,750°C. There are different kinds of thermocouples available based on their temperature range and limitations. The most commonly used thermocouples are J type thermocouples and K type thermocouples.
- Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD):
- RTD’s are also known as resistance thermometers. They detect the temperature by measuring the resistance of the RTD element. The resistance of the RTD element increases or decreases as the temperature increases or decreases. The metal used can be made of either platinum, nickel, or copper. There are two types of RTDs available: wire-wound type and thin-film type. RTDs cannot measure temperature as wide as Thermocouple and they are very precise in their measurements. A PT100 is a variety of an RTD, where PT refers to the material that the sensor is made of, which in this case is platinum and 100 means that the RTD has a resistance of 100 ohms at the temperature of 0°C.
- Thermistor:
Non-Contact Temperature Sensors
A non-contact temperature sensor is used to determine the temperature of the object without directly contacting a surface by using a technology that does not require any contact. The most common type of non-contact temperature sensors are thermal imaging and infrared sensors. They also include optical pyrometers, radiation thermometers and fiber optic sensors. Non-contact type temperature sensors are primarily used in dangerous or hazardous processes.
Temperature Sensor Range in Accuracy and Responsiveness
The accuracy of a temperature sensor is the highest difference between the actual value and the indicated value at the output of the sensor. Factors that can affect temperature sensor accuracy include linearity, repeatability, and stability. RTDs are the most accurate and stable temperature sensors and are more linear than thermocouples and thermistors. This is one of the primary reasons they are used when accuracy is critical while sensitivity and cost are less important.











